Flag of Djibouti
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2024) |
 | |
| Calanka Qaranka Agat Simbili علم الوطني Drapeau national ('National Flag') | |
| Use | National flag and ensign |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 2:3 |
| Adopted | June 27, 1977 |
| Design | A horizontal bicolour of light blue and light green, with a white isosceles triangle at the hoist bearing a red star in its center. |
The national flag of Djibouti[a] is a horizontal flag bicolor with equal bands of light blue and light green, with a white, equilateral triangle at the hoist. In the center of the triangle is a red star.[1] The flag combines the basic layout and colors from the flag of the Front de Libération de la Côte des Somalis. The light blue represents the sky and the sea, as well as the Somalis, green represents the everlasting green of the earth, as well as the Afars, white represents the colour of peace and the five point red star represents unity, the blood shed by the martyrs of independence, as well as Djibouti being one of the five regions inhabited by the Somali people.
History
[edit]Beginning in the mid-19th century before the establishment of the French Somaliland, other flags were used as the flag of the Ottoman Empire, Sultanate of Tajoura and as well religious flags.[2] During the French Somaliland and French Territory of the Afars and the Issas, the only ensign used was the tricolor. The flag was created and designed by the Front for the Liberation of the Somali Coast (FLCS) as the party official flag in the 1960s, which was a guerrilla group who fought for the independence of Djibouti from France. With the help of Ligue Populaire Africaine pour l'Indépendance (LPAI) to independence in 1977.[2] The Djiboutian flag was raised for the first time upon independence on 27 June 1977,[2] by the head of police Yacine Yabeh Galab. It is today flown on many governmental buildings.
Characteristics
[edit]Specifically, this flag consists of two horizontal bands sky blue and green, and a white isosceles triangle located on the side of the pole. In the middle of the triangle, a red five-pointed star appears.
The meaning of this flag is also found in the national anthem of Djibouti, with some differences:
- Sky blue: "symbolizes Bab el-Mandeb and the Gulf of Tadjourah, however the national anthem references the blue of the sky."
- Green: "symbolizes the earth, expressed by the eternal green of the earth."
- Red: "symbolizes the blood shed by the martyrs of independence."
- White: "symbolic white of peace"
In the middle of the triangle, a red five-pointed star symbolizes national unity.[1]
Color
[edit]Note: as there is no official standard, the below are approximations.
(1977–present) |
Sky Light Blue | Green | Red | White |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pantone | 284c | 354c | 185c | White |
| CMYK | 59-11-0-0 | 77-0-100-0 | 0-86-63-0 | 0-0-0-0 |
| RGB | 106-178-231 | 18-173-43 | 215-20-26 | 255-255-255 |
| Hexadecimal | #6AB2E7 | #12AD2B | #D7141A | #FFFFFF |

Historical flags
[edit]
The following are the flags historically used in the territory of present-day Djibouti:
-
 Flag of the Adal Sultanate (1415–1577)
Flag of the Adal Sultanate (1415–1577) -
 Flag of the Ottoman Empire (1577–1793), used when Habesh Eyalet included part of present-day Djibouti.
Flag of the Ottoman Empire (1577–1793), used when Habesh Eyalet included part of present-day Djibouti. -
 Flag of the Khedivate of Egypt (1874–1881), used when the Khedivate's Somali Coast included part of present-day Djibouti.
Flag of the Khedivate of Egypt (1874–1881), used when the Khedivate's Somali Coast included part of present-day Djibouti. -
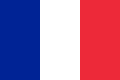
 Flag of France, used between 1896 and 1977, as French Somaliland is the predecessor to today's Djibouti.
Flag of France, used between 1896 and 1977, as French Somaliland is the predecessor to today's Djibouti.
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Anjali Kamath. Flag Book. Popular Prakashan. p. 19. ISBN 978-81-7991-512-7.
- ^ a b c "flag of Djibouti". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 15 September 2014.