Turkish makam
The Turkish makam (Turkish: makam pl. makamlar; from the Arabic word maqam مقام) is a system of melody types used in Turkish classical music and Turkish folk music. It provides a complex set of rules for composing and performance. Each makam specifies a unique intervalic structure (cinsler meaning genera) and melodic development (seyir).[1] Whether a fixed composition (beste, şarkı, peşrev, âyin, etc.) or a spontaneous composition (gazel, taksim, recitation of Kuran-ı Kerim, Mevlid, etc.), all attempt to follow the melody type. The rhythmic counterpart of makam in Turkish music is usul.
Geographic and cultural relations
[edit]The Turkish makam system has some corresponding relationships to maqams in Arabic music and echos in Byzantine music. Some theories suggest the origin of the makam to be the city of Mosul in Iraq. "Mula Othman Al-Musili," in reference to his city of origin, is said to have served in the Ottoman Palace in Istanbul and influenced Turkish Ottoman music. More distant modal relatives include those of Central Asian Turkic musics such as Uyghur “muqam” and Uzbek shashmakom. North and South Indian classical raga-based music employs similar modal principles. Some scholars find echoes of Turkish makam in former Ottoman provinces of the Balkans.[2] All of these concepts roughly correspond to mode in Western classical music, although their compositional rules vary.
Similarities between Turkish classical and folk music
[edit]Turkish classical music and Turkish folk music are both based on modal systems. Makam is the name of the scale in classical music, while Ayak (Ayağı) is the name of the scale in folk music. Makam and Ayak are similar; following are some examples:
- Yahyalı Kerem Ayağı: Hüseyni Makamı
- Garip Ayağı: Hicaz Makamı
- Düz Kerem Ayağı: Karcığar Makamı
- Yanık Kerem Ayağı: Nikriz Makamı
- Muhalif Ayağı: Segâh Makamı
- Tatyan Kerem Ayağı: Hüzzam Makamı
- Misket Ayağı: Eviç Makamı
- Bozlak Ayağı: Kürdî Makamı
- Kalenderi Ayağı: Sabâ Makamı
- Müstezat veya Beşirî Ayağı: Mahur Makamı
There are some similarities between the rhythms used in Turkish folk music and Turkish classical music, with respect to their forms, classification, and rhythmic patterns.[3]
Makam building blocks
[edit]Commas and accidentals
[edit]
In Turkish music theory, the octave is divided into 53 equal intervals known as commas (koma), specifically the Holdrian comma. Each whole tone is an interval equivalent to nine commas. The following figure gives the comma values of Turkish accidentals. In the context of the Arab maqam, this system is not of equal temperament. In fact, in the Western system of temperament, C-sharp and D-flat—which are functionally the same tone—are equivalent to 4.5 commas in the Turkish system; thus, they fall directly in the center of the line depicted above.
Notes
[edit]Unlike in Western music, where the note C, for example, is called 'C' regardless of what octave it might be in, in the Turkish system the notes are – for the most part – individually named (although many are variations on a basic name); this can be seen in the following table, which covers the notes from middle C ("Kaba Çârgâh", C4) to the same note two octaves above ("Tîz Çârgâh", C6):
The following table gives the tones over two octaves (ordered from highest to lowest), the pitch in commas and cents relative to the lowest note (equivalent to Western middle C), along with the nearest equivalent equal-temperament tone. The tones of the Çârgâh scale are shown in bold.
Tone name Commas
above middle CCents
above middle CArel-Ezgi-Uzdilek
notation of 53-ΤΕΤ toneNearest equivalent
12-ΤΕΤ toneTîz Çârgâh 106 2400 C6 C6 Tîz Dik Bûselik 105 2377 C 
6C6 Tîz Bûselik 102 2309 B5 B5 Tîz Segâh 101 2287 A 
5 / B
5B5 Dik Sünbüle 98 2219 A 
5 / B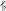
5A♯
5 / B♭
5Sünbüle 97 2196 A♯
5 / B♭
5A♯
5 / B♭
5Muhayyer 93 2106 A5 A5 Dik Şehnâz 92 2083 G 
5 / A
5A5 Şehnâz 89 2015 G 
5 / A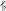
5G♯
5 / A♭
5Nim Şehnâz 88 1992 G♯
5 / A♭
5G♯
5 / A♭
5Gerdâniye 84 1902 G5 G5 Dik Mâhûr 83 1879 F 
5 / G
5G5 Mâhûr 80 1811 F 
5 / G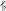
5F♯
5 / G♭
5Eviç 79 1789 F♯
5 / G♭
5F♯
5 / G♭
5Dik Acem 76 1721 F 
5 / G
5F5 Acem 75 1698 F5 F5 Hüseynî 71 1608 E5 E5 Dik Hisâr 70 1585 D 
5 / E
5E5 Hisâr 67 1517 D 
5 / E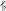
5D♯
5 / E♭
5Nim Hisâr 66 1494 D♯
5 / E♭
5D♯
5 / E♭
5Nevâ 62 1404 D5 D5 Dik Hicâz 61 1381 C 
5 / D
5D5 Hicâz 58 1313 C 
5 / D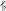
5C♯
5 / D♭
5Nim Hicâz 57 1291 C♯
5 / D♭
5C♯
5 / D♭
5Çârgâh 53 1200 C5 C5 Dik Bûselik 52 1177 C 
5C5 Bûselik 49 1109 B4 B4 Segâh 48 1087 A 
4 / B
4B4 Dik Kürdi 45 1019 A 
4 / B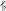
4A♯
4 / B♭
4Kürdi 44 996 A♯
4 / B♭
4A♯
4 / B♭
4Dügâh 40 906 A 4 A4 Dik Zirgüle 39 883 G 
4 / A
4A4 Zirgüle 36 815 G 
4 / A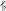
4G♯
4 / A♭
4Nim Zirgüle 35 792 G♯
4 / A♭
4G♯
4 / A♭
4Rast 31 702 G4 G4 Dik Gevest 30 679 F 
4 / G
4G4 Gevest 27 611 F 
4 / G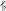
4F♯
4 / G♭
4Irak 26 589 F♯
4 / G♭
4F♯
4 / G♭
4Dik Acem Aşîrân 23 521 F 
4 / G
4F4 Acem Aşîrân 22 498 F4 F4 Hüseynî Aşîrân 18 408 E4 E4 Kaba Dik Hisâr 17 385 D 
4 / E
4E4 Kaba Hisâr 14 317 D 
4 / E
4D♯
4 / E♭
4Kaba Nim Hisâr 13 294 D♯
4 / E♭
4D♯
4 / E♭
4Yegâh 9 204 D4 D4 Kaba Dik Hicâz 8 181 C 
4 / D
4D4 Kaba Hicâz 5 113 C 
4 / D
4C♯
4 / D♭
4Kaba Nim Hicâz 4 91 C♯
4 / D♭
4C♯
4 / D♭
4Kaba Çârgâh 0 0 C4 C4
Intervals
[edit]The names and symbols of the different intervals (şifre) are shown in the following table:
| Interval Name (Aralığın adı) |
Value in terms of commas (Koma olarak değeri) |
Symbol (Simge) |
|---|---|---|
| koma or fazla | 1 | F |
| eksik bakiye | 3 | E |
| bakiye | 4 | B |
| küçük (sağir) mücenneb | 5 | S |
| büyük (kebir) mücenneb | 8 | K |
| tanîni | 9 | T |
| artık ikili | 12 - 13 | A |
Tetrachords (dörtlüler) and pentachords (beşliler)
[edit]
Similar to the construction of maqamat noted above, a makam in Turkish music is built of a tetrachord built atop a pentachord, or vice versa. Trichords exist, e.g. Saba, but are rarely used. Additionally, most makams have what is known as a "development" (genişleme in Turkish), which can occur either above or below (or both) the tonic and/or the highest note.
There are six basic tetrachords, named sometimes according to their tonic note and sometimes according to the tetrachord's most distinctive note:
- Çârgâh
- Bûselik
- Kürdî
- Uşşâk
- Hicaz and
- Rast
There are also six basic pentachords with the same names with a tone (T) appended.
It is worth keeping in mind that these patterns can be transposed to any note in the scale, so that the tonic A (Dügâh) of the Hicaz tetrachord, for example, can be moved up a major second (9 commas) to B (Bûselik), or in fact to any other note. The other notes of the tetrachord, of course, are also transposed along with the tonic, allowing the pattern to preserve its character.
Basic makam theory
[edit]A makam, more than simply a selection of notes and intervals, is essentially a guide to compositional structure: any composition in a given makam will move through the notes of that makam in a more or less ordered way. This pattern is known in Turkish as seyir (meaning, "route"), and there are three types of seyir:
- Ascending (çıkıcı);
- Descending (inici);
- Descending-ascending (inici-çıkıcı)
Makams are built of a tetrachord plus a pentachord (or vice versa), and in terms of this construction, there are three important notes in the makam:
- The durak ("tonic"), which is the initial note of the first tetrachord or pentachord and which always concludes any piece written in the makam.
- The güçlü ("dominant"), which is the first note of the second tetrachord or pentachord, and which is used as a temporary tonic in the middle of a piece (in this sense, it is somewhat similar to the axial pitches mentioned above in the context of Arab music). This use of the term "dominant" is not to be confused with the Western dominant; while the güçlü is often the fifth scale degree, it can just as often be the fourth, and occasionally the third.
- The yeden ("leading tone"), which is most often the penultimate note of any piece and which resolves into the tonic; this is sometimes close to an actual Western leading tone (either slightly sharper or slightly flatter) and sometimes close to a Western subtonic.
Additionally, there are three types of makam as a whole:
- Simple makams (Basit makamlar), almost all of which have a rising seyir,
- Transposed makams (Göçürülmüş/Şed makamlar), which as the name implies are the simple makams transposed to a different tonic,
- Compound makams (Bileşik/Mürekkeb makamlar), which are a joining of differing makams and number in the hundreds.
Some simple makams
[edit]Bûselik makam
[edit]This makam has two basic forms: in the first basic form (1), it consists of a Bûselik pentachord plus a Kürdî tetrachord on the note Hüseynî (E) and is essentially the same as the Western A minor; in the second (2), it consists of a Bûselik pentachord plus a Hicaz tetrachord on Hüseynî (E) and is identical to A harmonic minor. The tonic is A (Dügâh), the dominant Hüseynî (E), and the leading tone G-sharp (Nim Zirgüle). Additionally, when descending from the octave towards the tonic, the sixth (F, Acem) is sometimes sharpened to become F-sharp (Dik Acem), and the dominant (E, Hüseynî) flattened four commas to the note Hisar (1A). All these alternatives are shown below:
Çârgâh makam
[edit]This makam is thought to be identical to the Western C-major scale, but actually it is misleading to conceptualize a makam through Western music scales. Çârgâh makam consists of a Çârgâh pentachord and a Çârgâh tetrachord starting on the note Gerdâniye (G). Thus, the tonic is C (Çârgâh), the dominant is G (Gerdâniye), and the leading tone is B (Bûselik).
The çârgâh makam has at certain points in history been criticized for being a clumsy and unpleasant makam that can inspire those listening to it to engage in delinquency of various kinds.[dubious – discuss]
Hicaz makam
[edit]Rast makam
[edit]This much-used makam - which is said to bring happiness and tranquility to the hearerer - consists of a Rast pentachord plus a Rast tetrachord on the note Neva (D); this is labeled (1) below. The tonic is G (Rast), the dominant D (Neva), and the leading tone F-sharp (Irak). However, when descending from the octave towards the tonic, the leading tone is always flattened 4 commas to the note Acem (F), and thus a Bûselik tetrachord replaces the Rast tetrachord; this is labeled (2) below. Additionally, there is a development (genişleme) in the makam's lower register, below the tonic, which consists of a Rast tetrachord on the note D (Yegâh); this is labeled (1A) below.
In Turkey, the particular Muslim call to prayer (or ezan in Turkish) which occurs in the afternoon and is called Ikindi, as well as the day's final call to prayer called Yatsı, are often recited using the Rast makam.
Kürdî makam
[edit]Rast makam
[edit]Uşşâk makam
[edit]This makam consists of an Uşşâk tetrachord plus a Bûselik pentachord on the note Neva (D); this is labelled (1) below. The tonic is A (Dügâh), the dominant—here actually a subdominant—is D (Neva), and the leading tone—here actually a subtonic—is G (Rast). Additionally, there is a development in the makam's lower register, which consists of a Rast pentachord on the note D (Yegâh); this is labeled (1A) below.
In Turkey, the particular call to prayer which occurs around noon and is called Öğle is most often recited using the Uşşak makam.
See also
[edit]- List of Turkish makams
- List of notes in Turkish makam theory
- Rhythm in Turkish music
- Ottoman music
- Persian dastgah
- Arabic maqam
- Music of Turkey
- Turkish music (style)
Notes
[edit]- ^ Beken and Signell 2006,[page needed].
- ^ Shupo, Sokol, ed., Urban Music in the Balkans. Tirana:ASMUS, 2006
- ^ "https://www.pegem.net:TÜRK MUSİKÎSİ TEORİK VE UYGULAMALI BİLGİLERİNİN, EĞİTİM VE ÖĞRETİMDE VERİLEBİLMESİNE İLİŞKİN BİR MODEL ÖNERİSİ" (PDF). Retrieved 26 March 2017.
Sources
[edit]- Beken, Münir, and Karl Signell. "Confirming, delaying, and deceptive elements in Turkish improvisation," Maqām Traditions of Turkic Peoples: Proceedings of the Fourth Meeting of the ICTM Study Group "maqām", Istanbul, 18–24 October 1998, edited by Jürgen Elsner and Gisa Jähnishen, in collaboration with Theodor Ogger and Ildar Kharissov, [page needed] Berlin: trafo verlag Dr. Wolfgang Weist, 2006. ISBN 3-89626-657-8 http://www.umbc.edu/eol/makam/2008Kongre/confirming.html
Further reading
[edit]- Aydemir, Murat. Turkish music makam guide. Pan Yayıncılık, 2010. ISBN 9789944396844.
- Mikosch, Thomas. Makamlar: The Musical Scales of Turkey. S.l.: Lulu.com, 2017. ISBN 978-0244325602.
- Özkan, İsmail Hakkı. Türk Mûsıkîsi Nazariyatı ve Usûlleri. Kudüm Velveleleri. Ötüken, 2000. ISBN 975-437-017-6.
- Signell, Karl L. Makam: Modal Practice in Turkish Art Music. Nokomis FL (USA): Usul editions/Lulu.com., 2004. ISBN 0-9760455-0-8. "Unabridged reprint of the 1986 hard cover edition with updates, corrections, introduction, audio and other supplements". Originally published: Asian Music Publications, Series D: Monographs, no. 4. Seattle: Asian Music Publications, 1977.
- Signell, Karl L. Makam: Türk Sanat Musikisinde Makam Uygulaması (Turkish translation of above). Istanbul: Yapı Kredi Kültür Sanat Yayıncılık, 2006. ISBN 975-08-1080-5.
- Yılmaz, Zeki. Türk Mûsıkîsi Dersleri. Istanbul: Çağlar Yayınları, 2001. ISBN 975-95729-1-5.
External links
[edit]- Klasik Türk (Tasavvuf) Musikisi İlahi Peşrev Saz semaisi ve Taksim nota ve mp3 kayıtları
- Cinuçen Tanrıkorur, "The Ottoman Music", translated by Savaş Ş. Barkçin, https://web.archive.org/web/20061215165158/http://www.turkmusikisi.com/osmanli_musikisi/the_ottoman_music.htm
- Maqam World
- Sephardic Pizmonim Project- Jewish use of Makam










